OUTLINE
Unlike industrial products, harvested agricultural products are ‘ alive creatures ‘ that consume their own nutrients through physiological functions such as respiration, transpiration, and ethylene production, and are easily altered. Therefore, in order to preserve taste and nutrients, ‘ Drying ‘ process is required. Drying is the process of removing moisture. Although the moisture content at harvest varies depending on the agricultural products, it is generally about 30% for cereals and over 70% for fruit and vegetables. Therefore, a considerable amount of energy (latent heat of water evaporation) is required for drying, 50% for cereals, and 20% for fruit and vegetables. Therefore, it is the core of the drying technology to reduce the drying cost while preventing the deterioration of the quality of agricultural products. LifeNTech provide optimal drying solutions by studying the physical properties of agricultural products, analyzing the flow of hot air, and drying far infrared rays.
Moisure Evaparation Latent Heat Calculation Example
The energy required to evaporate the water contained in agricultural products, that is, the latent heat of evaporation of water, is 10 to 30% larger than the latent heat of evaporation of free water and tends to increase as the water content decrease. This is because the lower the water content, the stronger the moisture defects in agricultural products.
- Red pepper per hour
When 1 ton dry(edifice 175kg) - Amount of water to be removed : 824kg/h(When the initial moisture content is 85% and the final moisture content is 15%)
- Free water evaporation latent heat : 2,360kJ/kg (When the drying temperature is 60℃)
- Water evaporation latent heat for drying of red pepper : 824kg/hX2,360kJ/kgX1.2=2,333,568kJ/kg=648KW
Optimal Drying Design With Hich Quality & High Efficiency
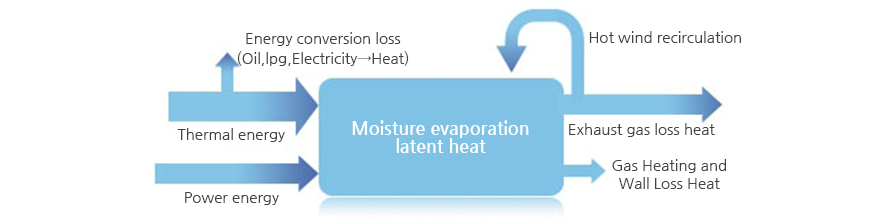
Considering the energy balance of the dryer, the proportion of latent heat of evaporation that is actually used for drying is not high because a significant portion of the input heat energy is lost through exhaust gas, raw material temperature rise, gas heating and gas wall. Therefore, in order to improve the drying efficiency, it is necessary to design such as reducing heat loss as much as possible and recirculating the exhaust gas. However, in general, high drying efficiency dose not guarantee quality. In some cased, drying efficiency tends to deteriorate when efficiency is increased. For example, when the hot air recirculation is increased, the heat loss decrease, but the drying time becomes longer and the quality deteriorates Therefore, in order to achieve high-quality, high-efficiency drying, optimization of hot air temperature, air flow rate and recycling hot air is required.
Far-Infrared Drying
In addition to the design of the dryer, you can use relatively inexpensive LPG or electricity instead of oil as a heat source (Fuel) or use a far-infrared drying method instead of a hot air drying method to reduce drying costs. In particular, far-infrared drying has the advantage of high efficiency by heating the object without energy loss due to heat transfer through radiation, but it also has difficulties to solve the drying deviation due to the limited penetration depth and straightness.
Installation Picture
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Drying Line | Electrical Heater & Fan | Electrical Control Panel | Red-Pepper Drying Techinology Concept Outline |
